What is IVF Pregnancy?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex process in which eggs and sperm are fertilized in a lab. Once an embryo (fertilized egg) is formed, the specialist will place it in the uterus. Using the procedure, multiple eggs are extracted using a transvaginal ultrasound-guided needle and mixed with sperm cells in a petri dish.
IVF Success Rate
IVF is very effective. The IVF success rate depends on a set of factors, including your age, when you get the procedure done, the cause of infertility, the choice of frozen or fresh eggs, or whether eggs are donated or are your own, to name a few.
Multiple treatment cycles increase the odds and result in a higher IVF success rate.
In the latest report from the CDC on Assisted Reproductive Technology 2018, USA [DGSK1] , 50 percent of IVF procedures in women aged 35 and under resulted in a live birth. For women between 40-42, 3.9 percent of the egg transfers resulted in a successful conception.
Read about: Top 6 Things You Should Avoid if You Want to Conceive
What Happens Before IVF Treatment Procedure?
Before In vitro fertilization starts, there are several things that your doctor may want to do.
- Take birth control pills – This might seem counterintuitive since you are trying to conceive, but research has found that in certain people it improves the chance of a successful IVF procedure.
- Assess and improve your general health. Especially if you have a known medical condition e.g., Thyroid disease or Vitamin D deficiency.
An Overview of the IVF Process
In-vitro fertilization involves several different steps. The process takes approximately two to three weeks. Here’s an overview.
- Ovarian Stimulation and Monitoring: The first step of IVF involves ovarian stimulation. Stimulations typically last anywhere between eight and 14 days. During regular ovulation, just one egg is mature enough to ovulate. To boost your chances of conceiving, IVF specialists use a process called controlled ovarian stimulation. , Stimulation helps boost the ovulation process to make several eggs available, making it more likely that you will conceive. During stimulation, your ovaries’ response to the medications will be monitored via blood tests and transvaginal ultrasound. Monitoring is very important because it can help your doctor determine whether or not the medications are working or need to be adjusted. Monitoring can occur daily or several times a week over two weeks.
- Egg Retrieval: About 36 hours after your last hormone injection, or “Trigger Shot,” the eggs will be retrieved. During this process, called a follicular aspiration, a very thin needle is guided into your ovaries to remove the eggs. This is a minor procedure typically performed in the operating room. You will receive mild sedation and pain medication to reduce your discomfort during the process. In some cases, a general anesthetic may be used. Once the needle is guided into your ovaries, it will pull eggs out using a special suction device that is attached. The eggs are then placed in a solution and put in an incubator. After retrieval, your physician may place you on progesterone supplements.
- Sperm Collection: Your partner will be asked to provide a sperm sample on the day of your egg retrieval or you will have chosen a donor sperm sample beforehand, The sperm are then separated in the laboratory from the semen fluid, and the healthiest ones are chosen to fertilize the eggs.
- Fertilization: After the eggs are removed from your ovaries, they will be fertilized. This step is also called insemination. There are two different types of insemination:
- Conventional insemination. This is the type of insemination that people are most familiar with. During this type of fertilization, mature eggs, and healthy sperm are mixed and incubated overnight in the lab.
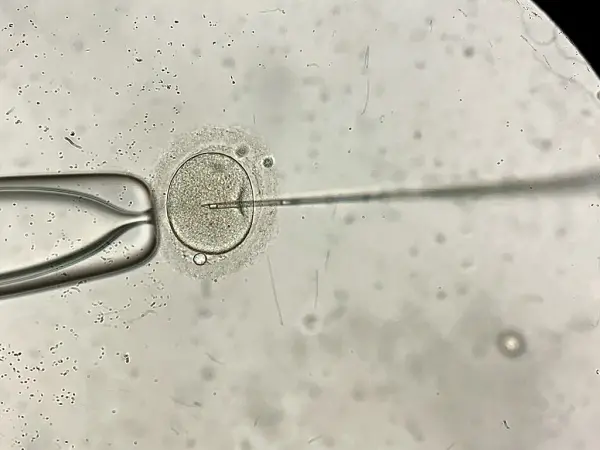
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Sometimes a healthy sperm is directly injected into each mature egg. This type of insemination is used when sperm number or quality is low or if prior IVF cycles fail.
- Embryo Transfer: About three to five days after egg removal, your doctor will look for the healthiest embryos to be transferred to the uterus. This is a procedure that is typically painless, although you may rarely be given a mild sedative. You will be awake during the procedure. You may experience some mild cramping. Your doctor will place the embryos back into your uterus using a thin catheter.
The goal is for at least one embryo to implant itself in the lining of your uterus and begin to develop. Sometimes women who use IVF have multiples because more than one embryo ends up implanting.
After the IVF Process
This is the final step you have been waiting for. Wondering how to calculate pregnancy weeks after IVF? From 12 days to two weeks after egg removal, your physician will test a blood sample to determine whether you’re pregnant. If the pregnancy test is positive, your doctor may ask you to continue with progesterone supplements for several weeks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About IVF
Here are some of the most common questions we get asked at ART Fertility Clinics.
Do IVF cycle cancellations Occur?
An IVF cycle may sometimes be canceled if your fertility specialist feels that the cycle has no chance of producing a successful outcome. The risk of cancellation is higher with age, particularly if you are older than 35.
What Are the Risks of IVF?
Because IVF is a complex set of procedures, there are some risks. Although working closely with your fertility expert can decrease the risks.
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome – This condition arises from using fertility drugs during IVF treatment. It can cause your ovaries to become painful and swollen.
- Multiple births – There is a greater chance of multiple births during IVF if more than one embryo is transferred.
- Infection – There is a small risk of infection from the egg retrieval process.
- Mental health issues – The process of IVF can be stressful. That’s why seeing a therapist is a good idea for anyone undergoing IVF. At ART Fertility clinics we have dedicated counselors available for supporting our patients in each clinic.
Make sure you talk to your fertility specialist about the risks of IVF before getting started.
What Can I Do if IVF Treatment Fails?
If IVF fails, you will want to talk to your fertility specialist. The doctor will help you understand the reasons and the best options for you. Don’t lose hope because there are many advances in fertility treatments.
Final Thoughts from ART Fertility
Having one failed IVF cycle does not mean you cannot get pregnant. Remember, all IVF cycles do not succeed, therefore doing more than one cycle increases the probability or odds of success. You can still have many options even after a failed IVF treatment procedure. Do not lose hope!! If you have more questions, feel free to contact the doctors at ART Fertility Clinics.