You are browsing content specific to your location, some treatments may not be available:

Experienced, World-Renowned Doctors & Embryologists
Comprehensive range of services including personalized treatments, diagnosing and treating male and female infertility, genetic testing
Over 71 percent Pregnancy Rate (without egg or sperm donation)
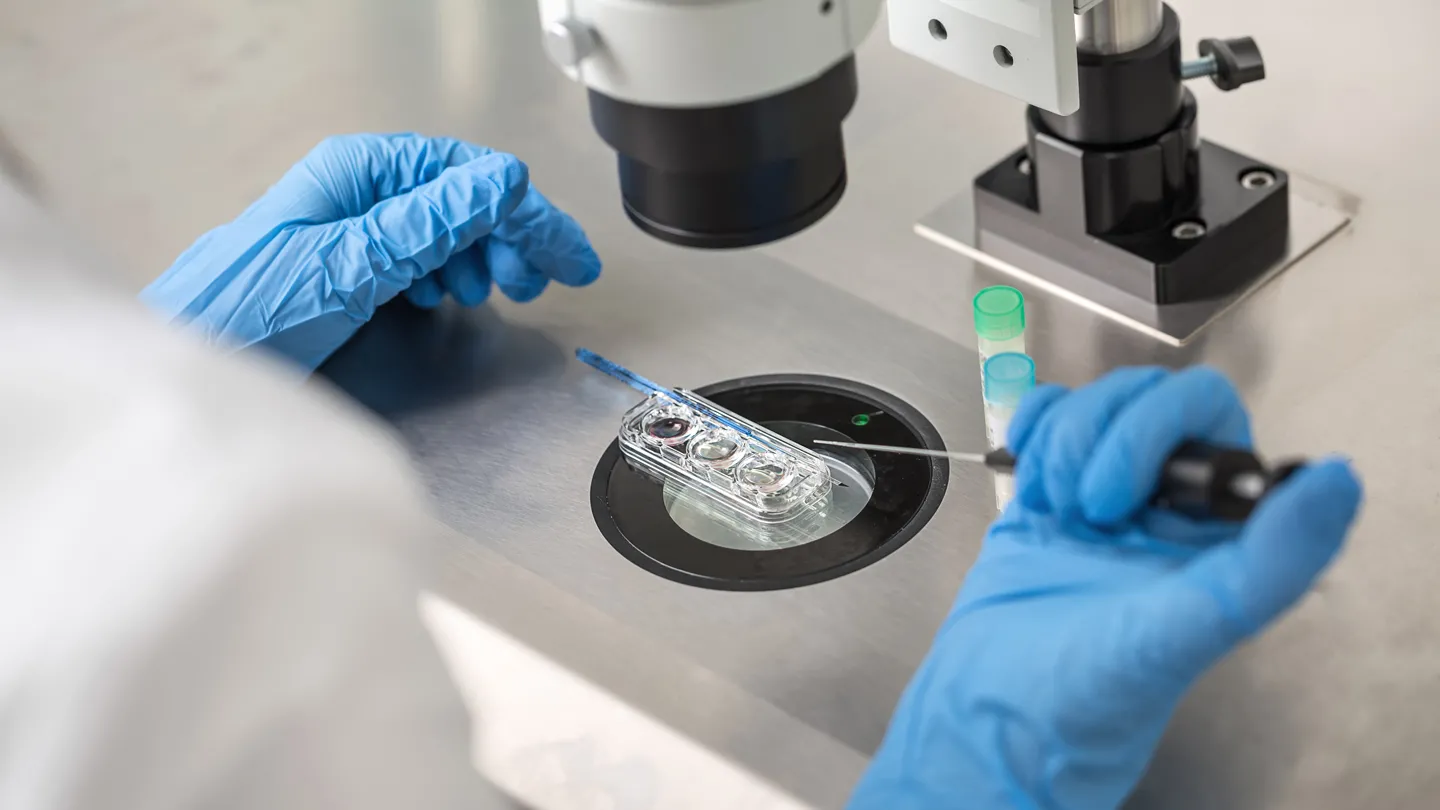
State-of-the-art equipment including
AI-enabled incubators, microscopes, 4 D Ultrasound machines.
Facilities include clean rooms, embryology, genetics lab & Air handling units that enable a healthy environment for embryo development.
Proprietary research and techniques that have been proven to enhance outcomes Peer reviewed publications in leading International journals

At ART Fertility we have designed all our medical services & protocols, patient care systems, and infrastructure on a patient-centric approach. We have achieved the highest levels of success rates (pregnancies and live births) whilst adhering to the most stringent safety standards.
WHY CHOOSE ART FERTILITY ?Fixed, published prices
No superfluous tests or procedures
Full access to medical & billing records
Highly trained medical staff
Nurses and professional counsellors to address medical needs and questions.
Single embryo transfer
Advanced computer systems that prevent mixing of sperm, eggs or embryos
Full time Anaesthetist
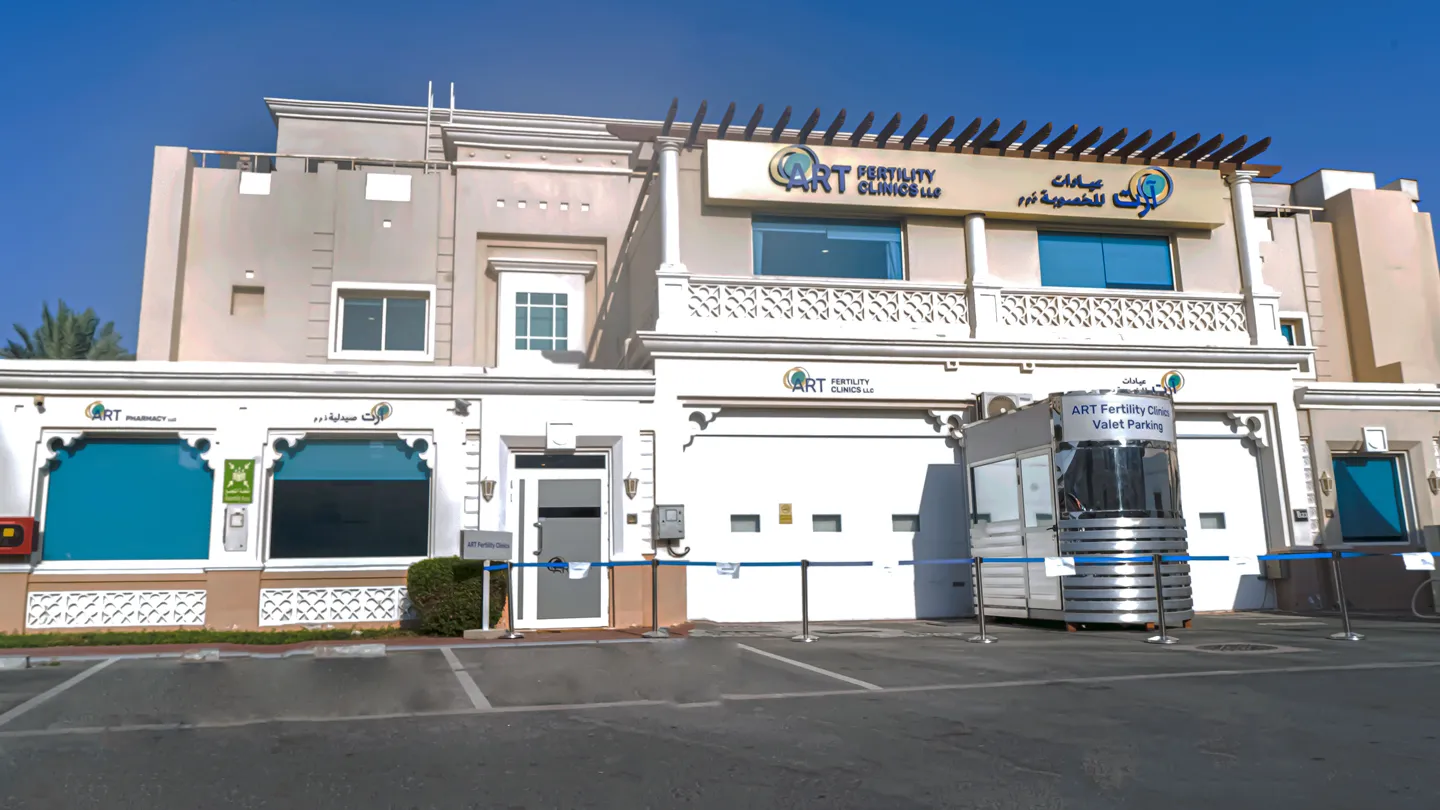


At ART Fertility Clinics in Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Al Ain & Muscat have helped thousands of couples achieve their dream of parenthood for delivering the highest success rate in the region. Team ART Fertility is here to help you make an informed decision.
The no. 1 IVF center in UAE is undoubtedly ART. When there was no hope, there was ART. PCOD and other male infertility factors caused us issues in conceiving and we stayed childless for 8 years of our marriage. With the help of expert doctors at ART and their attention and guidance, I could conceive my baby in the first attempt of the IVF process. Genetic screening of the embryos and trustworthy technology helped our imagination of having a healthy child into reality. Additionally, the clinic is very professional towards keeping the appointments on time as being a working couple it is hard to afford the time. IVF process is an extremely emotional journey also and ART-treated our journey with the right amounts of care and expertise. We are grateful to each team member of the ART clinic. Thank you so so much!.
From the moment that we commenced with ART, we felt we were in the hands of real professionals who had a genuine interest in assisting us in our desire to have a baby. Everything was clearly and properly explained and we felt that we were in good hands. After previous unsuccessful attempts with other Clinics, we noticed the difference. All the team was very supportive and extra special mention must go to Dr. Laura who was a great support, always there, and understood what we were going through. We would recommend ART for anyone looking to go ahead with IVF treatment..
"There is not enough gratitude and thanks we can give to the family of ART Fertility clinic. Our journey to happiness and Joy was a long and hard one but with their support, we never gave up and patience paid off. With the knowledge, experience, and guidance from Dr. Fatemi, the Care and the personal support from Dr. Laura, and all the wonderful people working there, we witnessed the amazing miracle of life and now have a bundle of joy in our life that filled it with unconditional love, laughter, and hope.".
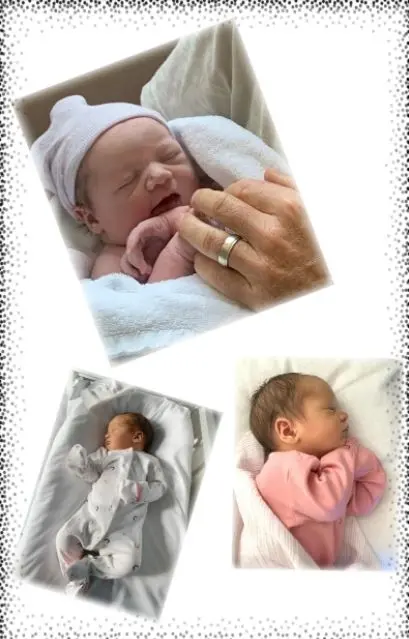
My name is Mariana and I have arrived all 3.49kg and 50cm tall in July 2021.
I have a great birth story. I was no problem for Mum. I was born in the water and had a little swim before Dad grabbed me and brought me to the surface. I am now at home with Mum and Dad. I think they like me around - in fact I think they are pretty chuffed :-)
I know that my journey to this world started more than 9 months ago and you all played a huge part in making it happen for me, Mum and Dad for which we will always be so deeply grateful.I am the lucky 4BB, day 6 blastocyst, transferred in Nov 2020 by Dr. Laura. Mum told me it was a great sunny day and all staff at the clinic were extremely nice. Dr. Laura and the nurse held my Mum’s hand and gave me and Mum all their positive thoughts, wishes and vibes.
Mum and Dad told me all about Prof. Fatemi, Dr. Barbara, Dr. Laura, Dr. Carol, Dr. Rachel, the embryologists and all the nurses and administrative staff at the clinic who were simply wonderful to us! I also know about Dr. Desi and the lovely staff at the Fetal clinic who supported Mum and Dad throughout our 9-month pregnancy journey and cared so much for my and Mum’s wellbeing.
Thank you for making my journey so cruisy and for everything you did for us so I could arrive safely. Apparently, they say I am pretty healthy and tick all the boxes. Mum and Dad had only great experiences with you all and consider themselves lucky to have been supported by such professional and thoughtful personnel at ART Clinics..
I would like to thank you for all your efforts and thank all the staff members and doctors as they are very helpful and respectful and they always care about patient satisfaction and are very supportive and I highly recommend people to visit your clinic and gain the 5-star treatment I would like to thank all the staff for everything as they are always supportive as I have been dealing with your clinic for years and I would never think to leave this clinic thank you again for everything
.
Our Specialists
Our Latest News and Publications
Our Happy Patients

 Call Us
Book an appointment
Call Us
Book an appointment
