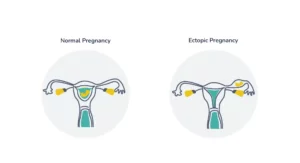
Ectopic Pregnancy
When the pregnancy occurs outside the womb, it is ectopic. This occurs because the embryo gets implanted outside the uterus. Sperm fertilizes the egg inside the fallopian tube in a natural pregnancy process. The conceived embryo moves via the tube. After 3 to 4 days, this embryo reaches the uterine cavity.
The embryo travels down the tube as a result of smooth muscle contractions of the fallopian tube. But, sometimes blockage or damage results in the tube. This prevents the embryo from reaching the womb, and implantation occurs in the tube. This results in tubal pregnancy.
An ectopic pregnancy frequently occurs in the fallopian tube. Implantation can also take place in abdominal areas, in the ovaries, or the cervix.
Who are at a greater risk of Ectopic pregnancy?
- These pregnancies can be associated with tubal diseases. The damage usually occurs due to a history of pelvic infections such as Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, or other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Females with a history of STI are more inclined to a risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Females who conceive after an episode of ectopic pregnancy are at a greater risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Other problems that enhance the risk include Endometriosis and diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure.
What are the symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy may experience symptoms of a standard pregnancy. The following signs might be useful in detecting a potential ectopic pregnancy:
- A positive pregnancy test and constant brown discharge or spotting.
- Irregular vaginal bleeding, lighter or heavier than the usual menses.
- High rectal pressure.
- Low blood pressure.
- Fainting, drowsiness, or weakness.
- Sharp or piercing pain.
If the ectopic pregnancy is detected at an early stage, then the complications can be reduced.
What is the diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy?
This pregnancy type is diagnosed by carrying out:
- Patient′s history examination (the last menses date).
- Assessment of the pregnancy hormone, hCG in the blood.
- Ultrasound of the uterine cavity.
- Pelvic examination for finding pain, tenderness, or mass in the abdominal area.
A pattern type increase is seen in the pregnancy hormone hCG. Ectopic pregnancies bring about a suboptimal development of the hCG. One can notice the pregnancy phase by looking at the value of hCG. If a blood test gives a specific hCG value and during Ultrasound, there is no pregnancy seen in the uterine cavity, then ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed. An irregular pregnancy (ectopic, future miscarriage) can be associated with low progesterone levels. For confirming ectopic pregnancy,Laparoscopy is required in few cases. This type of surgery evaluates the abdomen visually.
How to treat ectopic pregnancy?
- Watchful waiting: Careful monitoring of the patient’s condition must be done as no instant treatment can be given. Confine to females with early ectopic pregnancies, generally with no signs and low serum hCG levels (below 1,000 IU/L) without treatment. Numerous blood tests should be done to diagnose the fall in hCG levels. This signifies that the ectopic pregnancy is getting aborted on its own.
- Medication: Medical treatment can be given where hCG-level goes under 1500 IU/L and an ultrasonographic adnexal mass falls below the diameter of 3.5-4 cm. Medication named Methotrexate can be given to stop the development of ectopic pregnancy. After giving this medicine, careful monitoring of the patient is done for an hour. This medicine’s side effects may be nausea, vomiting, loose stools, mouth sores, abdominal pain, or drowsiness. After 5 days again, the patient’s hCG levels are examined. If there is severe abdominal pain within those 5 days, the patient must visit the hospital without delay.
- Surgery: Laparoscopy is frequently used. If an ectopic pregnancy diagnosis is made early prior to the tube’s rupturing, a Laparoscopic Salpingostomy might be done. In this technique, the fallopian tube is opened, and removal of the pregnancy tissue is done, and the tube is left in its place.
Is there any effect of ectopic pregnancy on fertility?
Yes, maybe. A female with a history of ectopic pregnancy has a greater risk of having another ectopic pregnancy. Also, her possibility of conceiving unexpectedly may reduce. However, most females still attain pregnancy successfully, either naturally or using Assisted Reproductive Technology, including IVF treatment.
What is the probability of another ectopic pregnancy?
Women have a 10 to 15% possibility of having another ectopic pregnancy after the first one. If the ectopic pregnancies keep recurring, then a surgical procedure can be done to block the fallopian tubes. This prevents an additional tubal pregnancy from occurring. Subsequently, they may undertake an IVF treatment.