Ovulation
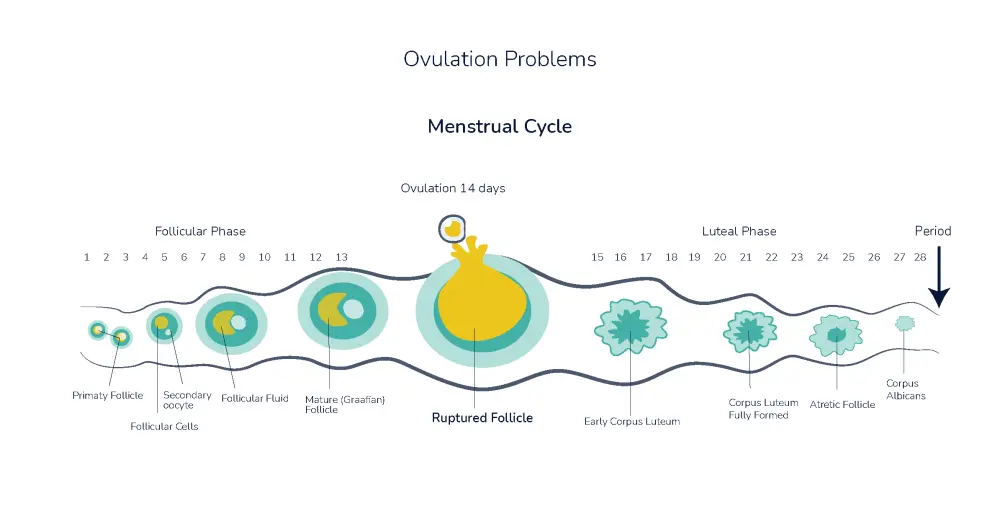
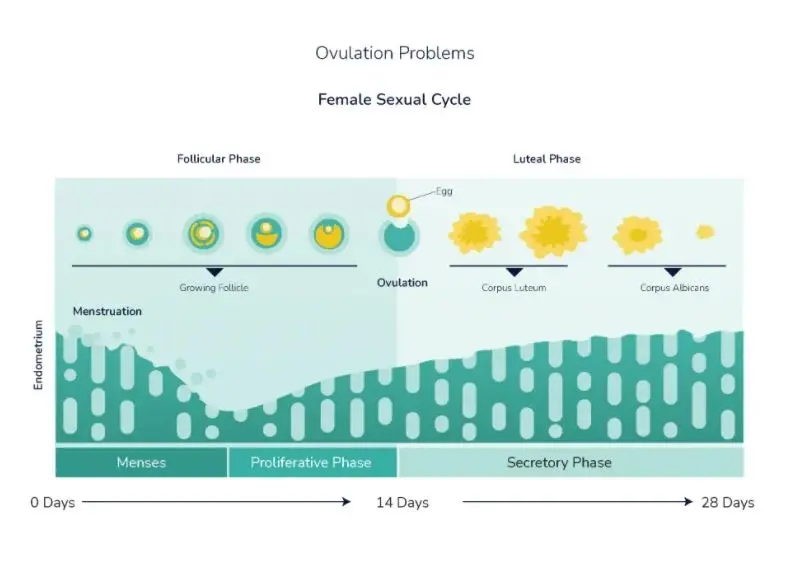
Ovulation is the process of releasing eggs from the ovaries. Generally, in a 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs approximately 14 days prior to the initiation of menses. Ovulation problems refer to the condition of an improper growth of the follicles or when the follicles cannot release a mature egg during the menses cycle. One of the major causes of infertility in females is the ovulation problem. About 25% of infertile females are experiencing specific issues with ovulation. Anovulation is the medical term used for the failure to produce and/or release eggs. In few cases, this occurs permanently, while in others, it emerges from time to time. Ovulation can be seen during few months, while in some months, it fails to occur.
What are the causes for such an ovulation problem?
A range of factors play a role in the arousal of ovulation problem:
- The most common reason being a hormonal imbalance. These hormones interact together to promote the growth of follicles and ovulation. These hormones play a crucial role in supporting the lining after the ovulation process. Their production occurs in the hypothalamus (a region present in the brain), ovaries, and glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
- Ovulation problems may also result due to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
- It may also occur because of too much exercise, stress, or weight loss/gain.
- Medications such as antidepressants, estrogen, and progestin may affect ovulation.
- Besides, a physical injury to the ovaries may bring about a failed ovulation.
How to diagnose ovulation problems?
- A complete physical examination is done.
- A thorough discussion on the history of menstrual cycles is also performed.
- Blood tests and Ultrasound of ovaries are also done.
- For confirming ovulation, an Ultrasound and a blood test are necessary during the menstrual cycle for clarifying whether ovulation is occurring or not.
What is the treatment?
The treatment depends on the reason behind the ovulation problem. Medicines might be recommended if the underlying cause involves a hormonal imbalance such as insulin or thyroid levels.
Fertility drugs that support ovulation are generally the first choice for females with unexplained ovulation problems. Difficulties with ovulation and fertility can pose significant challenges for individuals and couples who are trying to conceive. These challenges can stem from various underlying conditions or factors, such as hormonal imbalances, reproductive disorders, age, lifestyle habits, or environmental factors. Addressing and managing these challenges often requires a comprehensive approach that involves medical evaluation, lifestyle modifications, and/or assisted reproductive technologies, depending on the specific situation. By seeking timely and appropriate care, individuals and couples can increase their chances of achieving their fertility goals and starting or growing their families.
Ovulation Calculator
If you’re aiming to improve your chances of getting pregnant, one of the key pieces of information to keep in mind is when you’re ovulating. Ovulation refers to the point in your menstrual cycle when your ovary releases an egg, and it’s the time when you’re most likely to conceive. By tracking your ovulation, you can enhance your chances of becoming pregnant.
One useful tool for doing so is an ovulation calculator, which can assist you in pinpointing your ovulation window.